Nick ChimittI am a Research Scientist student at Purdue University. I received my PhD in Electrical and Computer Engineering from Purdue University, advised by Stanley H. Chan. My research involves machine learning, computer vision, computational imaging, image restoration, and differentiable optical modeling. Much of my earlier work involved imaging through atmospheric turbulence, and found its place in enabling better computer vision systems for recognition (face and body) in sequences distorted by turbulence by machine learning restoration. My current work involves broadening what I have developed in turbulence modeling and restoration to more general problems with implications for imaging through fog, rendering, and phase retrieval. Email / Google Scholar / |

|
BookMy PhD thesis was expanded into a book Computational Imaginag through Atmospheric Turbulence through NOW publishers and is available for FREE on arXiv. (Update Dec 17) For my dissertation, I am a recipient of the 2025 IEEE Signal Processing Society Best PhD Dissertation Award. Imaging through atmospheric turbulence is a field that can be traced back to Kolmogorov in the 1940's. The history of this topic is very rich, though the learning barrier to someone with a non-optics background is a major hurdle to overcome when approaching this problem. The purpose of this book, in part, is to lower this barrier of entry and provide the tools of modeling imaging through turbulence to a broader audience. |

|
Computational imaging through atmospheric turbulenceNicholas Chimitt, Stanley H. Chan NOW Foundations and Trends in Computer Graphics and Vision, 2023 arxiv / If you are a computer vision/computational imaging person interested in learning atmospheric turbulence modeling and restoration, this book is made for you. Test |
Research |

|
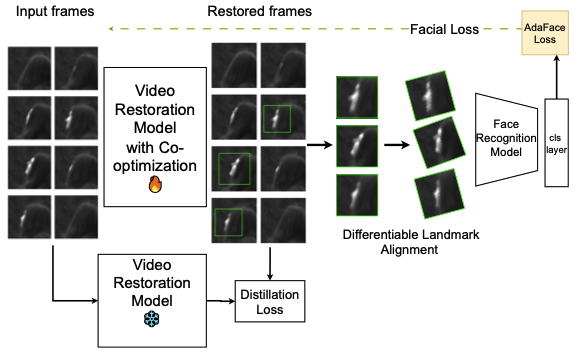
Restore What Matters: Lessons from Joint Restoration and RecognitionLanqing Guo1, Xijun Wang1, Minchul Kim1, Yu Yuan, Wes Robbins, Xingguang Zhang, Nicholas Chimitt, Stanley H. Chan, Zhangyang Wang, Xiaoming Liu (1Joint first author) Under Review, 2025 When solving a recognition problem, should we always restore the image before recognition? We find the answer is not so obvious. This paper seeks to answer this question with lessons learned from a multi-year IARPA project (BRIAR). |
|
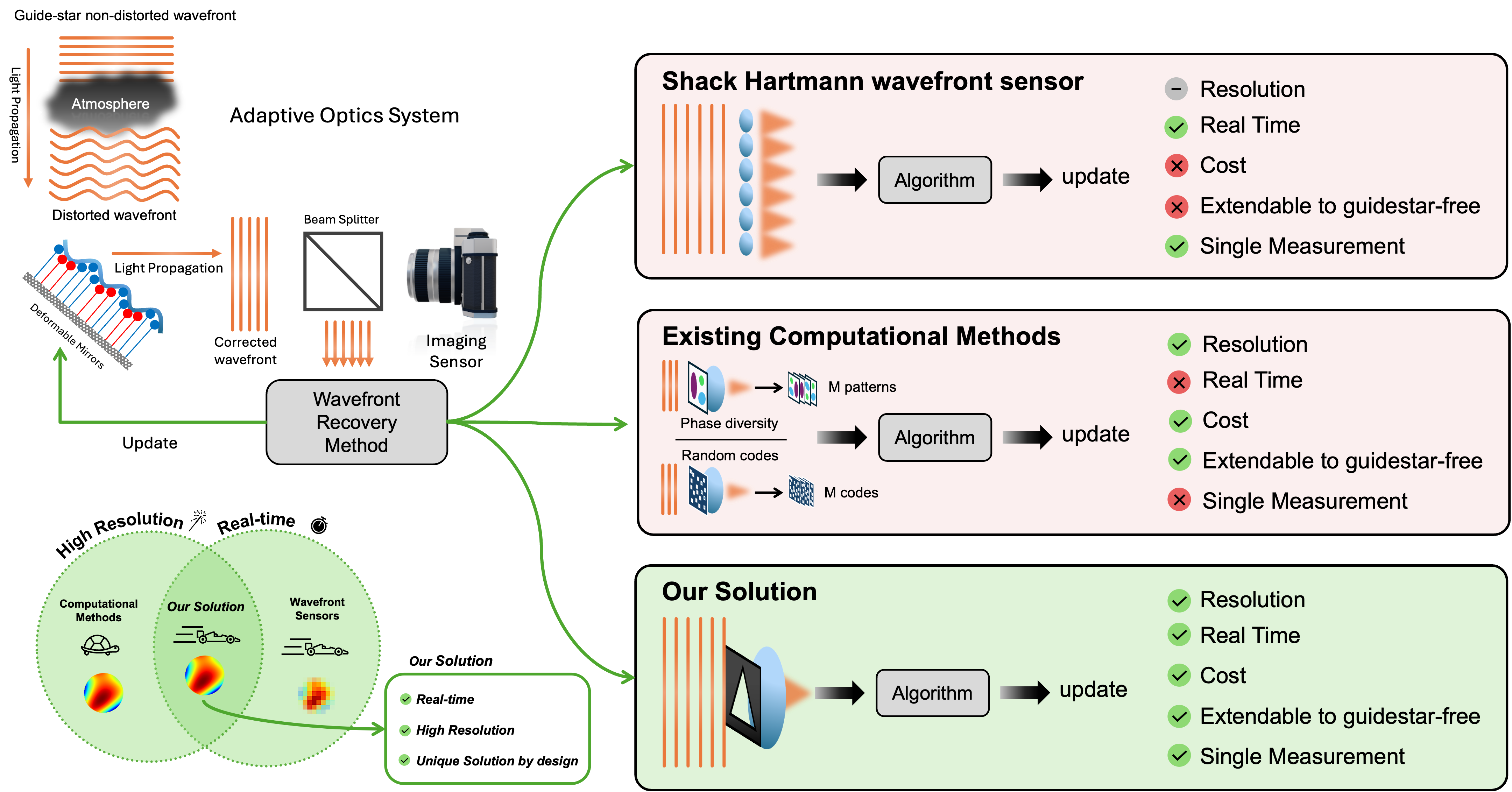
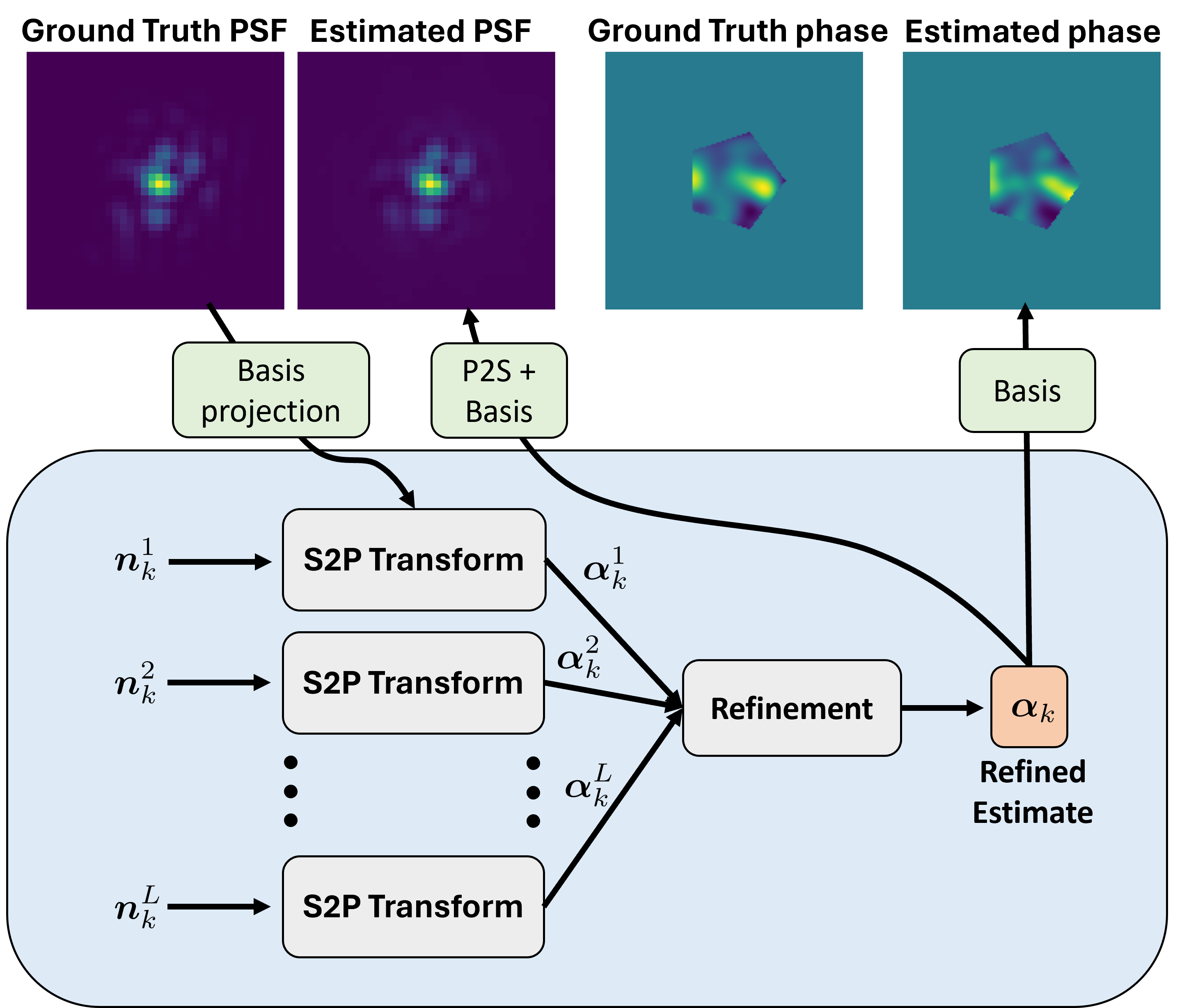
Wavefront Estimation From a Single Measurement Uniqueness and AlgorithmsNicholas Chimitt, Ali Almuallem, Qi Guo, Stanley H. Chan IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2025 arxiv / website / We theoretical show that pupil asymmetry can break ambiguities in the wavefront estimation/phase retrieval problem. We validate our theory using empirical and real optical bench data. |
|
(CVPR Highlight) Learning Phase Distortion with Selective State Space Models for Video Turbulence MitigationXingguang Zhang, Nicholas Chimitt, Xijun Wang, Yu Yuan, Stanley H. Chan Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2025 arxiv / code / website / A MAMBA-based restoration network that uses a latent phase distortion to model the turbulence distortion in a physically-motivated latent space. This combines the best of our two previous learning-based restoration algorithms. |
|
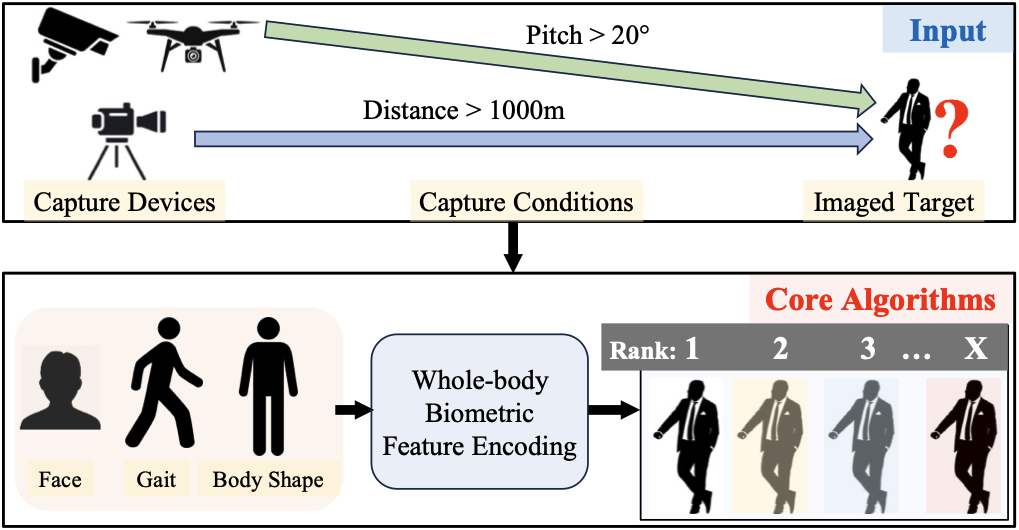
Person Recognition at Altitude and Range Fusion of Face, Body Shape and GaitFeng Liu, Nicholas Chimitt, Lanqing Guo, Jitesh Jain, Aditya Kane, Minchul Kim, Wes Robbins, Yiyang Su, Dingqiang Ye, Xingguang Zhang, Jie Zhu, Siddharth Satyakam, Christopher Perry, Stanley H Chan, Arun Ross, Humphrey Shi, Zhangyang Wang, Anil Jain, Xiaoming Liu Under Review, 2025 arxiv / The final computer vision recognition system resulting from a multi-university collaboration between Michigan State University, Georgia Tech, UT Austin, and Purdue for long range turbulence distorted face and body recognition. |
|
Phase retrieval of a point spread functionNicholas Chimitt, Ali Almuallem, Stanley H. Chan Unconventional Imaging, Sensing, and Adaptive Optics, 2024 pdf / We use the Phase-to-Space transform as a component of solving a phase retrieval problem. |
|
Scattering and gathering for spatially varying blursNicholas Chimitt, Xingguang Zhang, Yiheng Chi, Stanley H. Chan IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2024 arxiv / An analysis of two forms of spatially varying convolution and how they can be applied to different imaging or modeling problems. |

|
Imaging through the atmosphere using turbulence mitigation transformerXingguang Zhang, Nicholas Chimitt, Yiheng Chi, Zhiyuan Mao, Stanley H. Chan Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2024 arxiv / code / website / A transformer-based image restoration method that emphasizes a decomposition of the forward model to be reflected in the inverse process, first removing the tilt then removing the blur, consistent with the approximate atmospheric turbulence forward model. |
|
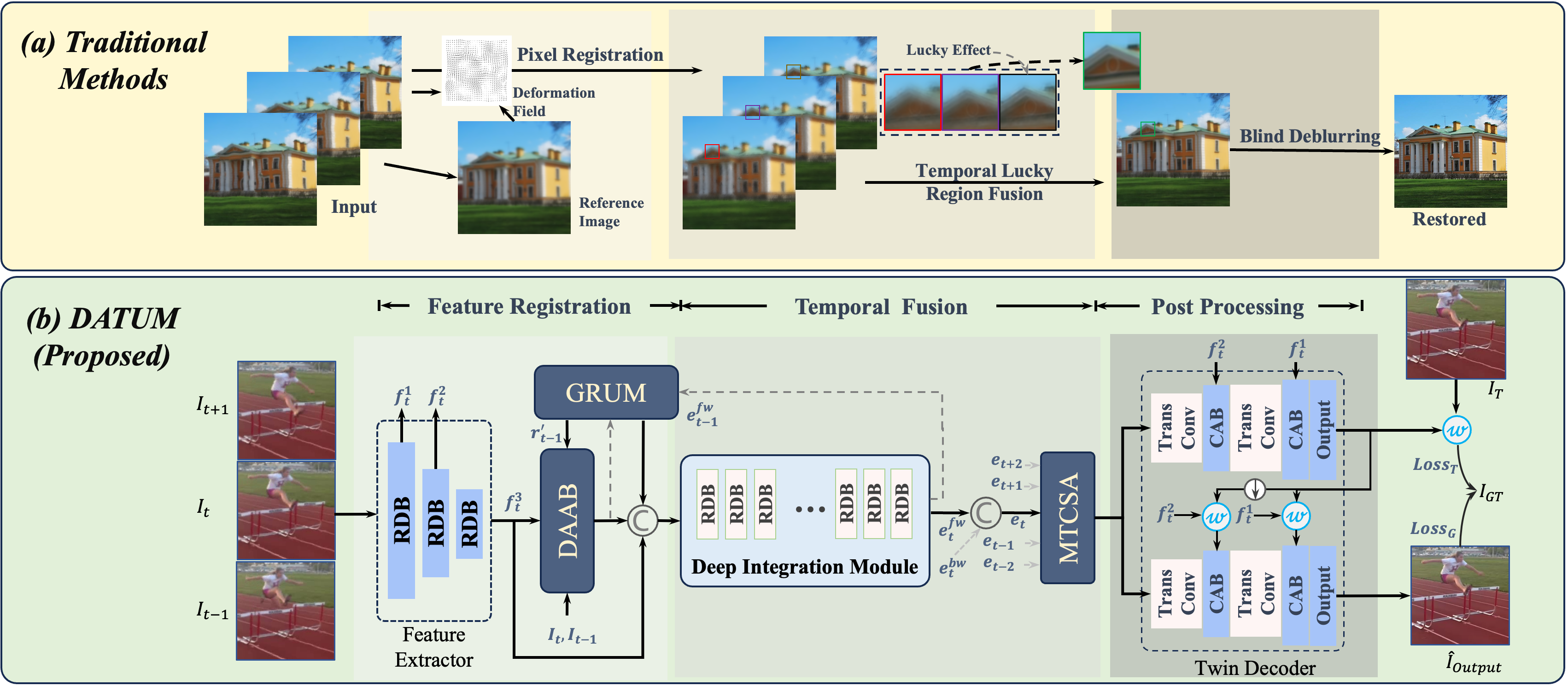
Spatio-temporal turbulence mitigation A translational perspectiveXingguang Zhang, Nicholas Chimitt, Yiheng Chi, Zhiyuan Mao, Stanley H. Chan Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2024 arxiv / code / website / A recurrent image restoration method that utilizes a large amount of frames, exploiting the turbulence lucky effect, to correct images distorted by turbulence. |
|
Farsight A physics-driven whole-body biometric system at large distance and altitudeFeng Liu, Ryan Ashbaugh, Nicholas Chimitt, Najmul Hassan, Ali Hassani, Ajay Jaiswal, Minchul Kim, Zhiyuan Mao, Christopher Perry, Zhiyuan Ren, Yiyang Su, Pegah Varghaei, Kai Wang, Xingguang Zhang, Stanley H. Chan, Arun Ross, Humphrey Shi, Zhangyang Wang, Anil Jain, Xiaoming Liu IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), 2024 arxiv / A multi-university collaboration regarding recognition of subjects at a distance that are distorted by atmospheric turbulence. Our simulation and restoration pipelines were found to improve recognition accuracy. |

|
Anisoplanatic optical turbulence simulation for near-continuous Cn2 profiles without wave propagationNicholas Chimitt, Stanley H. Chan SPIE Optical Engineering, 2023 arxiv / The original SPIE paper is revisited and an exact formula is derived, removing previous restrictions on the type of turbulence path distortions it can model. |
|
Real-time dense field phase-to-space simulation of imaging through atmospheric turbulenceNicholas Chimitt, Xingguang Zhang, Zhiyuan Mao, Stanley H. Chan IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2022 arxiv / We break previous restrictions in our simulations and design an approximate correlation structure to sample from that enables a per-pixel representation of the effects of imaging through turbulence. This method works in real-time for even 4k iamges. |

|
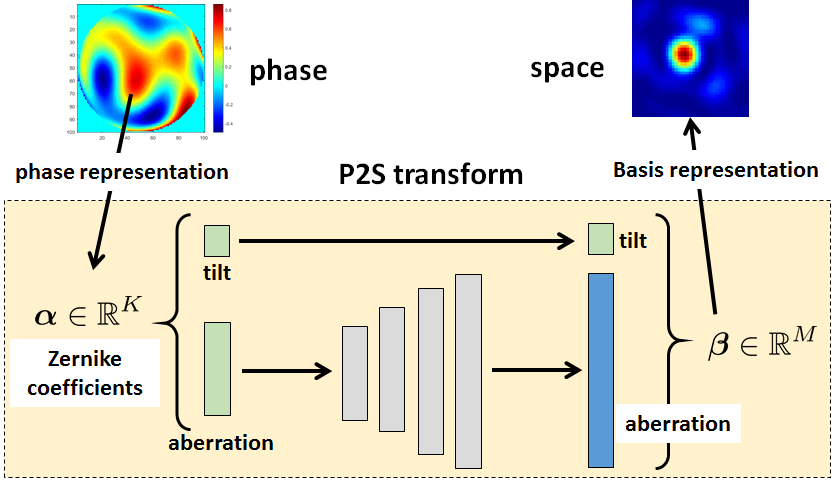
Accelerating atmospheric turbulence simulation via learned phase-to-space transformZhiyuan Mao, Nicholas Chimitt, Stanley H. Chan Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2021 arxiv / code / This paper introduces neural mappings to bridge gaps in simulation for atmospheric turbulence. We build a neural mapping to map from the phase representation (the phase domain) to the point spread function representation (the space domain) that we refer to as the Phase-to-Space (P2S) transform. |
|
Image reconstruction of static and dynamic scenes through anisoplanatic turbulenceZhiyuan Mao, Nicholas Chimitt, Stanley H. Chan IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2020 arxiv / code / A non-learning method for restoring images distorted by turbulence. While most methods focused on static scenes, our emphasize here was on dynamic scenes with moving images. |
|
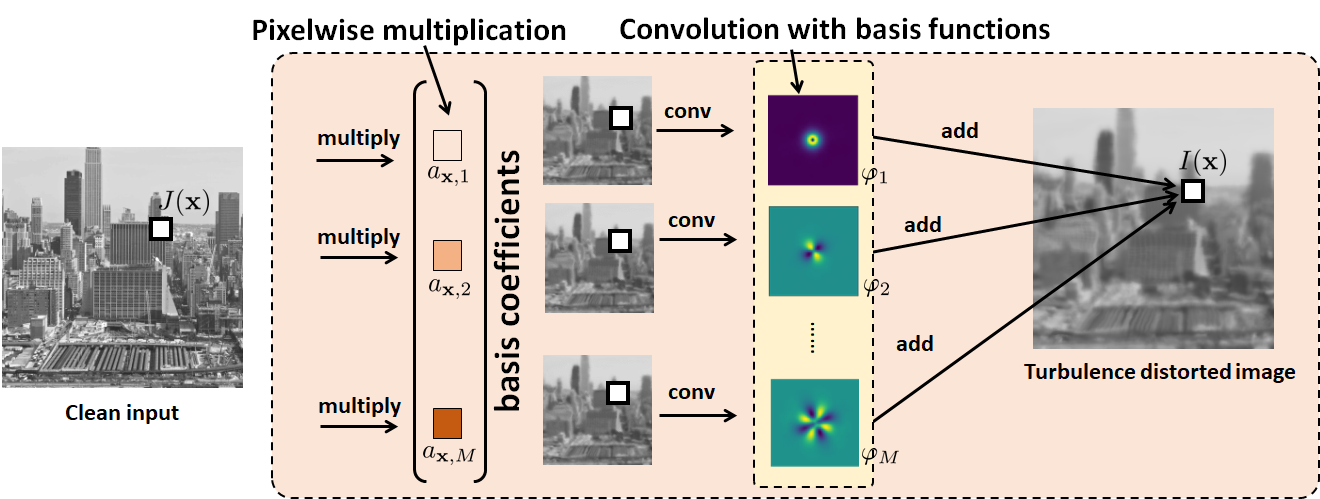
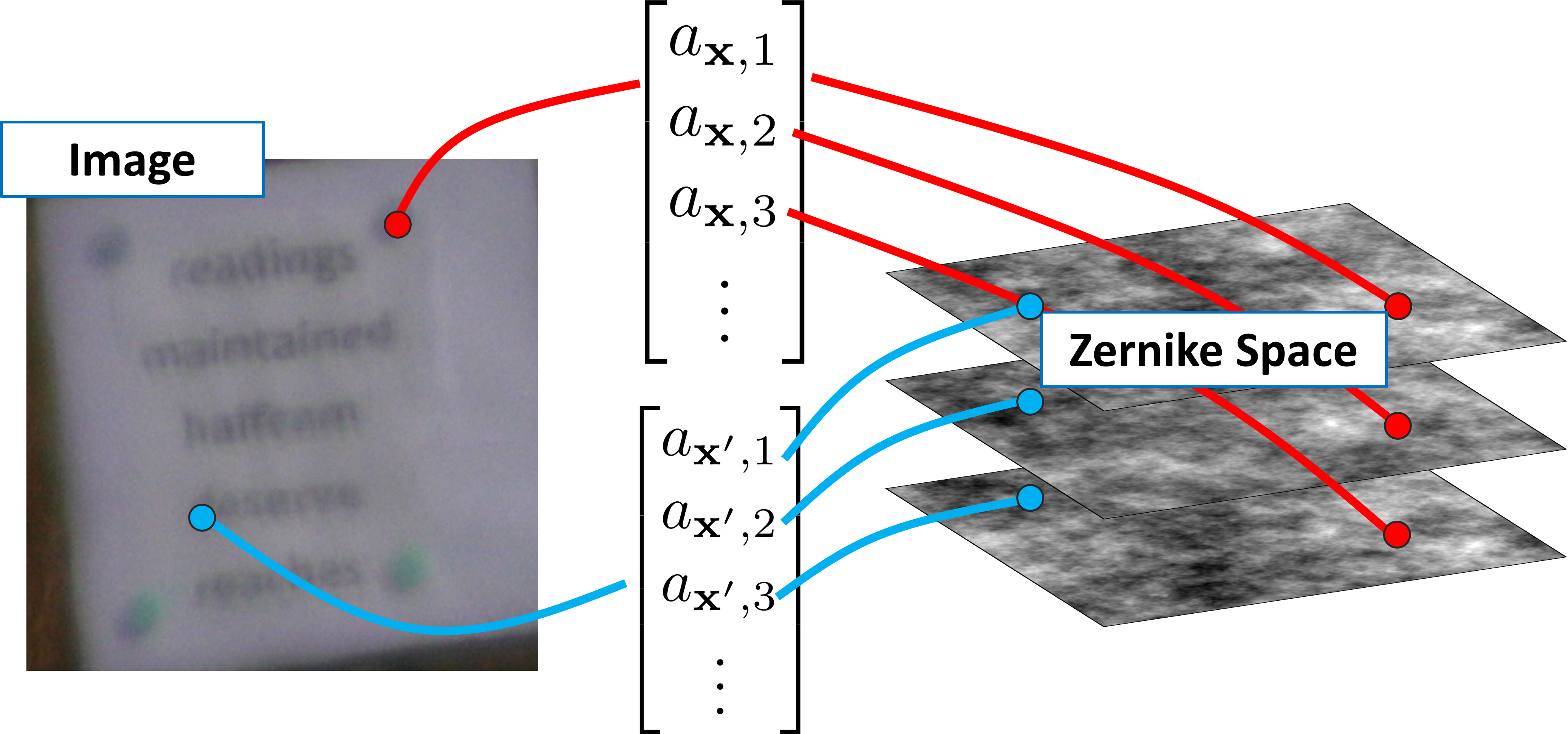
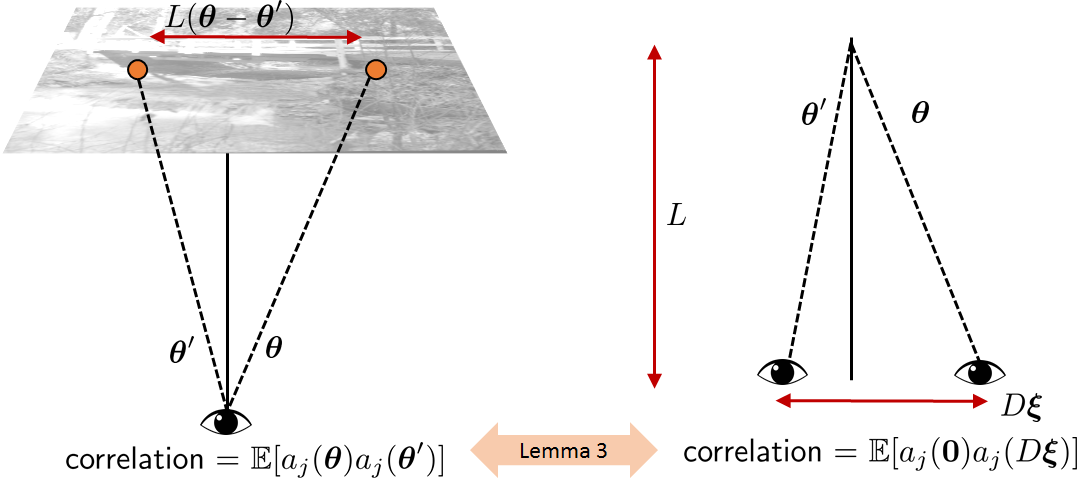
Simulating anisoplanatic turbulence by sampling intermodal and spatially correlated Zernike coefficientsNicholas Chimitt, Stanley H. Chan SPIE Optical Engineering, 2020 arxiv / code / The beginning of a series of papers on simulating imaging through atmospheric turbulence. We derive under an approximation the effect of turbulence on an image that is consistent with wave propagation models. |
Other ProjectsUnder construction... |
|
Design and source code from Jon Barron's website |